2016, June: Rationale for continued study of Radioimmunotherapy
Catch 22:
What is radio-immunotherapy (RIT)?
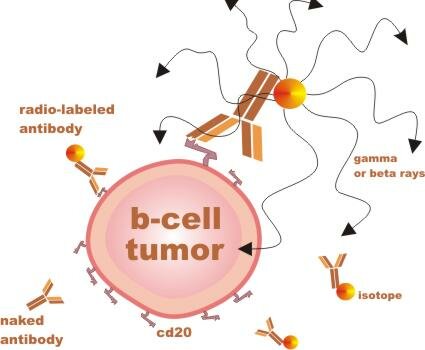 When your body detects something that does not belong, such as bacteria (pathogen), one way it eliminates the threat is to produce antibodies that bind to the protein shapes that are specific to the pathogen. When your body detects something that does not belong, such as bacteria (pathogen), one way it eliminates the threat is to produce antibodies that bind to the protein shapes that are specific to the pathogen.
RIT agents are man-made antibodies with different radiation components attached. These antibodies are designed to bind to a protein shape called CD20, which sticks out of mature B lymphocytes (immune cells), both malignant and nonmalignant (cancerous and normal). ...
... Importantly, the cd20 shape (or antigen / receptor) is not found on precursor B cells - immature b-cells which can later mature to replenish the supply of normal mature b-cells.
RIT is considered a targeted therapy, because the antibodies that deliver the radiation are specific to one type of cell. RIT is more potent than unlabeled antibody therapy, such as Rituxan, but it also has unique potential risks.
Importantly, there is clinical data showing that RIT is very potent and can induce complete responses that are very durable (measured in years), even in heavily pretreated patients. (See RIT abstracts below.)
RIT is given in therapeutic steps
(1) The initial antibody dose ("cold" or "naked" antibody) clears the body of normal b-cells so that subsequent doses will be more focused on tumor cells.
(2) The second "warm" dose has anti-tumor effects, but also helps calculate the optimal final dose based on uptake of the drug and individual clearance rates as determined by imaging of the gamma radioactive element.
(3) The final "hot" dose has has the most potent anti-tumor effects, and is focused on tumor cells, because prior doses have cleared the body of normal b-cells.
Unique properties of RIT
- Zevalin is an FDA approved RIT for indolent lymphoma
- RIT has unique properties:
It takes about 1 week to give it, compared to many months of chemotherapy.
It's the only non-chemotherapy-based approach with a high rate of durable remissions
It's an important choice for patients:
- who must continue to work through or shortly after treatment
- who cannot tolerate chemotherapy, because of advanced age, or specific comorbidities
- who may prefer to limit the on-treatment side effects specific to chemotherapy
such as nausea, neuropathy, hair loss, gastric, and gastric and mucositis complications.
Possible mechanisms of action
When radio-labeled antibody binds to tumor cells it can cause tumor killing by
-
Apoptosis - programmed cell death triggered by the antibody
-
Complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) - where antibody fixes complement that kills the tumor cells
-
Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) - where effector cells (immune cells) kill the tumor cells
-
Ionizing radiation from the radioisotope damages the tumor cells, leading to cell death
-
Vaccine-like effect - leading to adaptive immunity against cells that may survive initial treatment
Other RIT Topics
Radioimmunotherapy Background Articles
.gif) |
Dec 2018: Radioimmunotherapy (RIT) for Follicular Lymphoma achieves long term lymphoma control in first line and at relapse: 8-year follow-up data of 281 patients from the international RIT-registry pat http://bit.ly/2EqigiA
|
.gif) |
Radioimmunotherapy with tositumomab and iodine-131 tositumomab for NHL http://bit.ly/bGdSCA
|
.gif) |
Radioimmunotherapy of Lymphoma: Ahead of Its Time or Past Its Sell-By Date? http://bit.ly/9x2RgL
Tim Martin Illidge, School of Cancer and Imaging Sciences, Manchester Academic Health Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom
"As we look to the future, few things are certain, but we can be sure that there will continue to be increasing numbers of patients with follicular lymphoma who are refractory to both chemotherapy and rituximab. For the latter group, there are compelling data that RIT can play an important role in both chemotherapy- and rituximab refractory disease, leading to high response rates with durable remissions."
|
.gif) |
Radioimmunotherapy review article http://bit.ly/d181ic
"Currently in the United States, RIT is mainly used in the salvage setting; however, emerging data suggest that to enhance patient benefit, RIT should be administered earlier in the treatment of follicular lymphoma. In an analysis of 1,177 patients treated with 131I-tositumomab, the ORR, CR rate, and duration of response decreased as the number of prior therapies increased."
|
.gif) |
Rationale for Consolidation to Improve Progression-Free Survival in Patients with Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma: A Review of the Evidence http://bit.ly/2ttiY3
"With the higher CR rates and longer Progression Free Survival (PFS) times observed in patients with FL and DLBCL, as well as encouraging early data from MZL and MCL consolidation trials, RIT appears to have an important role in the treatment of patients with NHL."
|
.gif) |
Radioimmunotherapy for Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma clinmedres.org
Arati V. Rao, MD, Gamal Akabani, PhD and David A. Rizzieri, MD
|
.gif) |
Perspectives on RIT therapy
Robert M. Sharkey, PhD; and David M. Goldenberg, ScD, MD interactive.snm.org
|
.gif) |
Radioimmunotherapy in the treatment of low grade b-cell lymphoma ash2003 PDF
|
.gif) |
|
.gif) |
Radioimmunotherapy of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: From Clinical Trials to Clinical Practice
Malik E. Juweid, MD http://jnm.snmjournals.org
|
.gif) |
Novel Concepts in Radioimmunotherapy for Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma www.cancernetwork.com
|
.gif) |
Randomized Controlled Trial of Zevalin Versus Rituximab Immunotherapy for Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Low-Grade, Follicular, or Transformed B-Cell NHL http://bit.ly/aoKHyQ
|
.gif) |
Multicenter Phase II Study of Bexxar for Chemotherapy-Relapsed/Refractory Low-Grade and Transformed Low-Grade B-Cell NHL http://bit.ly/aX3cZf
Forty-five of 47 patients were treated with a single dosimetric and therapeutic dose. Twenty-seven patients (57%) had a response. The response rate was similar in patients with low-grade (57%) or transformed low-grade (60%) NHL. The median duration of response was 9.9 months. Fifteen patients (32%) achieved a complete response (CR; 10 CRs and five clinical CRs), including five patients (50%) with transformed low-grade NHL. The median duration of CR was 19.9 months, and six patients have an ongoing CR. Treatment was well tolerated, with the principal toxicity being hematologic. The most common nonhematologic toxicities that were considered to be possibly related to the treatment included mild to moderate fatigue (32%), nausea (30%), fever (26%), vomiting (15%), infection (13%), pruritus (13%), and rash (13%). Additionally, one patient developed human-antimouse antibodies.
|
Potential Benefits and Risks: RIT Studies:
FDA approved indications for RIT: "for the treatment of relapsed or refractory low grade, follicular, or transformed B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL)."
Comparing Risks of RIT-based therapy with Chemo-Rituxan-based therapy?
RIT, like all cancer treatments, has risks which should be carefully considered when making treatment decisions.
It should be noted that it's not possible to avoid treatment risk (even delaying therapy has risks) and chemotherapy-based protocols can have risks similar to RIT.
At present it's not known which approach to treating indolent lymphomas is better (on average) for survival - an endpoint that FDA considers the only reliable measure for comparison because it accounts for both known and unknown positive and adverse effects.
The risk we take cannot be separated from the potential reward or from clinical necessity. When you sprint to escape an aggressive bear you increase the risk of breaking a leg, or having a cardiac event ... Similarly, how appropriate the risks we assume when selecting a therapy depends on the clinical circumstances and the goal of treatment.
Ultimately, only well-controlled studies with sufficient follow up will help to determine which treatment approach provides the better chance for optimal clinical benefit, and most likely - given the variation in the disease and patients - the optimal therapy for any person varies and will involve some chance.
As the reports below indicate RIT is perhaps the most potent agent we have at this time for indolent b-cell lymphomas, but it also has risks, such as low platelet counts, infections, bleeding, and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), and also hypothyroidism for bexxar. Noting that the latency (time it takes to develop and present) for MDS - a serious potential complication - can be quite long. However, it should be noted that the risk of MDS also exists for chemotherapy-based protocols.
"Two studies have evaluated the risk for myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia following RIT with either 90Y-ibritumomab or 131I-tositumomab. These retrospective analyses of large numbers of patients both showed that RIT did not produce a higher risk for MDS in comparison with similar patient populations treated with multiple chemotherapies alone [90, 91]. MDS has rarely been observed in patients treated upfront with RIT using 131I-tositumomab alone [63].
- Radiolabeled and Native Antibodies and the Prospect of Cure of Follicular Lymphoma http://bit.ly/7mcys1
|
See for technical safety information Bexxar | Zevalin
In your conversation with your doctor about risks and benefits, you might also inquire about what future therapies may be precluded (made no longer available) by use of RIT and what specific clinical factors (such as age, areas of involvement, previous therapies) may increase or reduce risk as described in the following technical paper.
* Prediction of Hematologic Toxicity After Radioimmunotherapy with I-Labeled jnm.snmjournals.org
* Subsequent therapy can be administered after tositumomab and iodine I-131 tositumomab for non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer. 2005 Dec 16; PMID: 16362977
* Re-Treatment With I-131 Tositumomab in Patients With Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Who Had Previously Responded to I-131 Tositumomab jco.ascopubs.org
* Specific Regimen Influences Risk of Myelodysplasia After Lymphoma Treatment BloodJournal
* Harvesting Stem Cells for Transplant in Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Patients Is Still Possible After Treatment with Bexxar news.cornell.edu
See also Factors that Influence Treatment Decisions
Background: A reason RIT is considered a vital therapy is that it is the first treatment proven to reverse the pattern of decreasing response and duration of response in indolent lymphomas. Durable remissions reduce the need for multiple toxic treatments, which have been found by experts* to result in diminished response rate and duration of response. Furthermore, achieving a durable remission can substantially improve quality of life independent of symptoms by reducing the anxiety associated with living with active or dormant disease - particularly when the improved duration of the remissions is measured in years, suggesting a chance of cure.
The following abstract describes the pattern of relapse for follicular lymphomas with standard therapy:
* Each Subsequent Therapy Results in Diminishing Response Rate and Duration of Response in Low Grade or Transformed Low Grade NHL ASCO 2001
"Evaluation of response and duration of response in these sixty patients to all prior chemotherapies re-confirmed the previously published experience showing diminished response and duration of response with each subsequent chemotherapy.
In this same patient population the duration of response to the most recent chemotherapy was 4 months. However, upon relapse, subsequent treatment with Bexxar (a type of RIT) provided a 10 month duration of response (p=<0.001 ). An independent radiology and oncology review panel confirmed these findings.
The high incidence of multiple relapses and the enduring decrease in both response and duration of response to subsequent therapy further reinforces the need for novel therapies for the treatment of LG or Transformed LG NHL. New treatment options are necessary to provide greater clinical benefit evidenced by both response and duration of response."
In the News:
.gif) |
ASH Paper, 2013: A Randomized Phase II Study Comparing Consolidation With a Single Dose Of <sup>90</Sup>y Ibritumomab Tiuxetan (Zevalin®) (Z) Vs. Maintenance With Rituximab (R) For Two Years In Patients With Newly Diagnosed Follicular Lymphoma (FL) Responding To R-CHOP.
Preliminary Results At 36 Months From Randomization http://bit.ly/17jNgpg
Patients with FL can have long time of survival, but disease progression typically occurs 3-5 years after initial treatment. Consolidation with Z after initial therapy has shown to improve progression-free survival (PFS) mainly in the pre-R era, whereas maintenance with R also has demonstrated a substantial benefit in terms of PFS in patients treated with immunochemotherapy.
In this setting, the Spanish intergroup PETHEMA/GELTAMO/GELCAB started a randomized phase 2 trial in order to compare the use of consolidation with Z vs. R maintenance in patients with FL responding to R-CHOP. From June 2008 to July 2010, 146 patients (66M/80F; median age, 55 years) were enrolled from 25 Spanish institutions in the randomized phase 2 trial ZAR2007
Main inclusion criteria were: FL grade 1, 2 or 3a, age 18-75 years, stages II-IV and need of treatment according to modified GELF criteria. Patients with FL grade 3b or transformed to DLBCL were excluded.
... The number of patients in PR after R-CHOP who reached CR during maintenance were 14 of 28 (50%) and 12 of 26 (46%) for arms A and B, respectively.
Two patients developed transformation to DLBCL at 8 (arm A) and 39 months (arm B) after randomization. During the maintenance period, patients receiving Z showed grade 3-4 neutropenia in 6 of 63 cases and grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia in 5 of 63, whereas these figures were 1 of 61 and 0 of 61 (p=0.05) for patients in arm B, respectively. No unexpected late toxicities have been reported.
Five patients have died during the follow-up due to the progression of lymphoma in all cases, with no differences between the arms (36-month OS, 98% vs. 95% for arms A and B, respectively). In conclusion, in patients with FL in response after R-CHOP, maintenance with R was superior to consolidation with Z in terms of PFS, with no differences in OS with the current follow-up.
Advocate comment: That Rituxan competes with Zevalin for binding to cd20 could work against Zevalin in this study design - where induction included 4 cycles of Rituxan. In the FIT study (leading to approval of Zevalin for this use) the induction therapy often did not include Rituxan. KarlS
|
.gif) |
Zevalin Consolidation of First Remission in Advanced-Stage Follicular Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: Median Follow-Up of 7.3 Years From the International, Randomized, Phase III First-Line Indolent Trial” http://bit.ly/1khWdEV
|
.gif) |
|
.gif) |
Radioimmunotherapy/Chemotherapy Combination Could Extend Survival in Some Patients with Advanced Lymphoma - The ASCO Post http://bit.ly/12IhK7G
|
.gif) |
Zevalin - Medscape: Renewed Interest in Ibritumomab for NHL
|
Reports on Outcomes
Update: Bexxar® Provides Years of Lasting Activity as Initial Therapy
in Follicular Lymphoma patient.cancerconsultants.com
* Overall survival at 10 years was 86%.
* Anticancer responses were achieved in 95% of patients.
* A complete disappearance of detectable cancer (complete remission)
was achieved in 75% of patients.
* The median time for cancer progression among patients who achieved
a complete remission was 9.2 years.
.gif) |
Targeted Radio-Immunotherapy with Bexxar Produces Durable Remissions in Patients
with Late Stage Low Grade Non-Hodgkin's Lymphomas.
Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2004;115:255-72. PMID: 17060972
Response rates were 56% (overall) and 30% (complete). With a median follow-up of 44.6 months,
30% of the patients achieved a long-term, durable response; median time to progressive disease
or death was 5 years.
|
.gif) |
Bexxar radioimmunotherapy for relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma:
updated results and long-term follow-up of the University of Michigan experience.
Blood. 2000 Aug 15;96(4):1259-66. PMID: 10942366 | Related abstracts
For all 42 responders, the median progression-free survival was 12 months, 20.3 for those with CR.
Seven patients remain in CR 3 to 5.7 years. Sixteen patients were re-treated after progression;
9 responded and 5 had a CR. Reversible hematologic toxicity was dose limiting.
|
.gif) |
Efficacy and safety of Bexxar in B-cell lymphoma, progressive after Rituxan.
J Clin Oncol. 2005 Feb 1;23(4):712-9. Epub 2004 Dec 21. PMID: 15613695
the OR and CR rates were 86% and 57%. Estimated 3-year Progression Free Survival (PFS) in
this subgroup was 48%, compared with 11% for all others (P = .002).
Transient grade 3 to 4 marrow toxicity was seen in 50% of patients. Two patients, one of whom received two subsequent chemotherapy regimens, developed secondary Myelodysplasia.
CONCLUSION: (131)I tositumomab is effective in CD20-positive lymphoma progressive after rituximab,
with a 65% OR rate and median Progression Free Survival (PFS) of 24.5 months for responders.
Patients with follicular grade 1 or 2 histology and tumors < or = 7 cm achieved very high OR and
CR rates, with 48% PFS at 3 years.
|
.gif) |
Bexxar: novel radioimmunotherapy for the treatment of low-grade and transformed low-grade
non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Oncologist. 2004;9(2):160-72. Review. PMID: 15047920
In clinical trials of Bexxar, objective response rates ranged from 54%-71% in heavily pretreated patients.
In the pivotal trial, the number of patients with a longer duration of response after treatment with Bexxar
was significantly greater than the number of patients with a longer duration of response after their
last qualifying chemotherapy regimen. In 76 newly diagnosed patients, the objective response
rate was 97%, and 63% of patients achieved complete responses.
|
.gif) |
A clinical and scientific overview of tositumomab (Zevalin) and iodine I 131 tositumomab (Bexxar).
Semin Oncol. 2003 Apr;30(2 Suppl 4):22-30. Review. PMID: 12728404
"these studies show that tositumomab and iodine I 131 tositumomab treatment is safe and
induces high response rates and durable remissions in heavily pretreated patients with
low-grade or transformed low-grade NHL"
|
.gif) |
Zevalin and Bexxar produces durable complete remissions in a subset of
heavily pretreated patients with low-grade and transformed non-Hodgkin's lymphomas.
J Clin Oncol. 2005 Oct 20;23(30):7565-73. Epub 2005 Sep 26. PMID: 16186600
Response rates in the five trials ranged from 47% to 68%; CR rates ranged from 20% to 38%.
With a median follow-up of 5.3 years, the 5-year progression-free survival was 17%.
Eighty-one (32%) of 250 patients had a time to progression of > or = 1 year
(termed durable response population). For the durable response population, 44% had not progressed
at > or = 2.5 to > or = 9.5 years and had a median duration of response of 45.8 months.
The median duration of complete response was not reached. The durable response population had many
poor prognostic characteristics, including bone marrow involvement (41%), bulky disease > or = 5 cm (49%),
and transformed histology (23%). Forty-three percent of the patients had been treated with more than four prior therapies and 36% had not responded to their most recent therapy.
|
.gif) |
Zevalin radioimmunotherapy produces high response rates and durable remissions
in patients with previously treated B-cell lymphoma.
Clin Lymphoma. 2004 Sep;5(2):98-101. PMID: 15453924 | Related abstracts
In patients achieving a CR/CRu, the median TTP was 24.7 months for patients treated
with 90Y ibritumomab tiuxetan compared with 13.2 months for rituximab-treated patients (P = 0.41),
and ongoing responses of > 5 years have been observed.
|
.gif) |
Durable responses after ibritumomab tiuxetan radioimmunotherapy (Zevalin) for
CD20+ B-cell lymphoma: long-term follow-up of a phase 1/2 study.
Blood. 2004 Jun 15;103(12):4429-31. Epub 2004 Mar 11. PMID: 15016644
"Nine patients (24% of responding patients) had a TTP of more than 3 years.
Long-term responders (> 5 years) have been identified."
|
.gif) |
Leonard JP, Zelenetz AD, Vose JM, et al. Iodine I 131 tositumomab (Bexxar) for patients with
low grade or transformed low grade NHL: complete response data.
Blood. 2000;96(suppl 1):728a. Abstract 3148.
Summary data on 251 patients treated on various phase 1 to 3 tositumomab trials from 1990 to 1999.
Those characteristics statistically associated with a lower probability of achieving CR include
bulky disease, prior chemotherapy, lack of response to last chemotherapy, and prior radiotherapy.
Nonetheless, CR rates of 30% (confirmed) to 35% (not confirmed) may be expected in the group
as a whole, with 3-year median duration of CR in those without confirmed CR and
almost 5 years in those with confirmed CR status.
|
.gif) |
Radioimmunotherapy: FIT to be applied? Randomized study shows improved PFS by 2 yrs in follicular lymphoma when given as consolidation for chemotherapy Medscape.com ( login req.)
n = The trial compared a single Zevalin treatment with observation in 414 patients with advanced (stage 3 or 4) follicular lymphoma who had achieved partial or complete remission after first-line chemotherapy. The choice of which chemotherapy regimen to use for induction was left to the physicians' discretion, and various combinations were used, including CVP, CHP, fludarabine, chlorambucil, and rituximab.
|
Contraindications for use of RIT
Some of these "cutoffs" may have changed since the post date
.gif) |
Bone marrow biopsy results:
.gif) |
Hypocellular bone marrow (<15% cellularity)
|
.gif) |
Marked reduction of bone marrow precursors
NOTE: The bone marrow findings must be within 30 days
|
|
.gif) |
Impaired bone marrow reserves as indicted by:
.gif) |
prior myeloablative therapies with ABM or PBSC transplantation
|
.gif) |
Platelet count < 100,000 cells/mm3 (or perhaps < 50,000 for Zevalin)
|
.gif) |
ANC (Neutrophil Count (Absolute)) < 1,500 cells/mm3
|
.gif) |
History of failed stem cell collection
|
|
.gif) |
Known type I hypersensitivity or anaphylactic reactions to murine (mouse) proteins (HAMA)
or to any component of the therapeutic regimen
|
.gif) |
Positive pregnancy test - test required for women of child-bearing age.
|
.gif) |
Serum Creatinine > 1.5 X the upper limit of normal
|
.gif) |
Previous external beam radiation involving >25% of the active bone marrow
|
.gif) |
Pregnancy and continuing breast feeding
|
.gif) |
Children and adolescents under 18 years of age
|
.gif) |
Prior bone marrow or stem cell transplantation (this is being studied)
|
Adapted from: interactive.snm.org | eanm.org pdf
FDA Label describing use for
.gif) |
Zevalin: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/125019s0194lbl.pdf
|
.gif) |
Bexxar: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/125011s0126lbl.pdf
|
RIT for the Elderly?
.gif) |
Bexxar is an Effective and Well Tolerated Therapy in Elderly Patients with NHL asco.org
CONCLUSION: Bexxar was efficacious and well tolerated in this population of elderly patients with NHL. Due to physiologic changes in the elderly, conventional chemotherapy may require dose-attenuation; however, Bexxar therapy provides pt-optimized dosing so that the same TBD is given for all age groups. This novel therapy provides a therapeutic choice for pts who may have limited therapeutic options.
|
When to Consider RIT? ... Patient Perspectives
When might RIT be appropriate ... indicated ... deserving of full consideration?
FDA approved indications for RIT: "for the treatment of relapsed or refractory low grade,
follicular, or transformed B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL)."
Also see our brochure on this topic: RIT.pdf
Important: Treatment decisions are complex and require input from well-trained, experienced lymphoma specialists. All therapies have risks and outcomes will vary. Please discuss the risks and benefits of all reasonable therapies when consulting your physician. Items below marked with * indicate investigational uses. See Locating RIT-Based Clinical Trials.
.gif) |
As first primary treatment, perhaps as an alternative to chemotherapy, particularly if chemotherapy is not indicated for you. *
|
.gif) |
As consolidation therapy? *
Consolidation therapy is a treatment given shortly after another treatment with the goal of improving on the response. (Also called sequential therapy.)
|
.gif) |
As second primary treatment, particularly following a short or insufficient response to prior treatment?
A primary treatment is one that is given with intent to achieve a significant and long lasting response, as opposed to palliative therapy where the goal might be to relieve symptoms.
|
.gif) |
When you have relapsed from prior treatment, and the goal of your next therapy is to achieve a durable complete remission.
|
.gif) |
As an alternative to stem cell transplantation (SCT), particularly if SCT is indicated, but not suitable for you because of age or other factors. *
|
.gif) |
As part of the conditioning therapy of stem cell transplantation? *
|
.gif) |
As an alternative to maintenance Rituxan
Maintenance is the regularly scheduled administration of Rituxan with the goal of maintaining the response to prior induction treatment.
|
.gif) |
When transformation is suspected and you are not a candidate for SCT, or combination chemotherapy, such as CHOP-Rituxan?
Transformation is a change in the indolent lymphoma cells that leads to more aggressive clinical behavior and/or resistance to standard treatment.
|
NOTE: Clearly, the selection of treatment should be based on individual clinical details, and a realistic assessment of the most appropriate treatment goal. We have a concern that for non-clinical reasons* RIT is not being considered in some clinical centers.
Non-clinical factors that may influence underutilization of RIT
.gif) |
Lack of awareness of the potential of RIT to result in higher remission
rates and duration of remission among patients and some oncologists.
|
.gif) |
When insurance carriers do not cover treatment out of network/area,
and the patient's treating physician does not offer nuclear medicine.
|
.gif) |
A conflict of interest (mostly unintended) that occurs when physicians cannot
offer the full range of therapies within their local practice.
|
.gif) |
When the potential risks of RIT are overestimated or not fully understood
by patients and physicians.
|
What is the most appropriate goal of treatment for RIT?
.gif) |
Our impression is that RIT is best used when the goal of treatment is to potentially
cure or obtain a durable complete remission ... and that may not be as appropriate as
management therapy, because it cannot be given at frequent intervals to control the disease.
Therefore, if you have bulky disease, you may want to consider de-bulking prior to use of RIT,
as lower tumor burden is associated with better and more durable outcomes (O. Press).
However, use of chemotherapy shortly before RIT could also increase risks of RIT
Pretreatment might also include stem cell harvesting.
|
.gif) |
Pretreatment (sequential therapy) can also improve the safety of RIT by
decreasing the % of bone marrow involvement as described here:
Radioimmunotherapy in the treatment of low grade b-cell lymphoma
www.cecity.com PDF
|
Please consider the above as ideas and factors that may guide the discussions with your
doctor and the outside experts you may consult. It should not be regarded as medical advice.
Questions and Comments for Experts
Comparing Sequential chemo-RIT with autologous SCT? We believe a study comparing the following protocols would answer an important clinical question, and would also be of interest to patients with high-risk lymphomas referred to a transplantation center:
Sequential HD chemo - (with harvesting), sequenced with RIT versus Autologous SCT
Importantly, harvesting of stem cells in the Sequential therapy arm of the study will facilitate subsequent use of SCT should be needed.
Data on Long-term outcomes: There's a need to conduct a meta-analysis that describes the potential long term benefits and risks of RIT across many studies. It appears that lacking this information, clinical decisions are defaulting to what is less toxic in the short term and offered at the patient's local center.
High Dose RIT as an alternative to SCT? When is high dose (HD) radioimmunotherapy indicated? Can HD radiotherapy be used outside a clinical trial in cases where it is indicated? Lay comment: One indication for HD RIT seems to be in preparation for stem cell transplants, especially when conditioning chemotherapy fails to achieve a remission.
Extranodal disease and RIT: Does mucosal (gastric MALT) or CNS involvement preclude the use of radioimmunotherapy?
Does spleen involvement preclude use of radioimmunotherapy?
Residual splenomegaly in a patient who has otherwise successfully responded in other sites following chemotherapy for lymphoma is another reason for performing a splenectomy. In these cases, the procedure may be performed for both diagnostic and therapeutic reasons; it can determine if the splenomegaly is due to persistent lymphoma, and should this be true, it can potentially eliminate the focus of residual disease. A less common indication for splenectomy that may be seen more frequently in the future is to allow patients to become eligible for enrollment onto novel treatment protocols. An example of this is in patients with lymphoma refractory to conventional chemotherapy who were treated with radioimmunotherapy using a radiolabelled anti-CD20 antibody.
In some of these patients, splenomegaly was found to complicate treatment, as the large organ served as an “antigen sink”, effectively decreasing the dose of radionuclide available to treat other sites of disease. Thus, pretreatment splenectomy may be indicated to eliminate this complicating factor.
Radioimmunotherapy for other types of lymphoma?
|